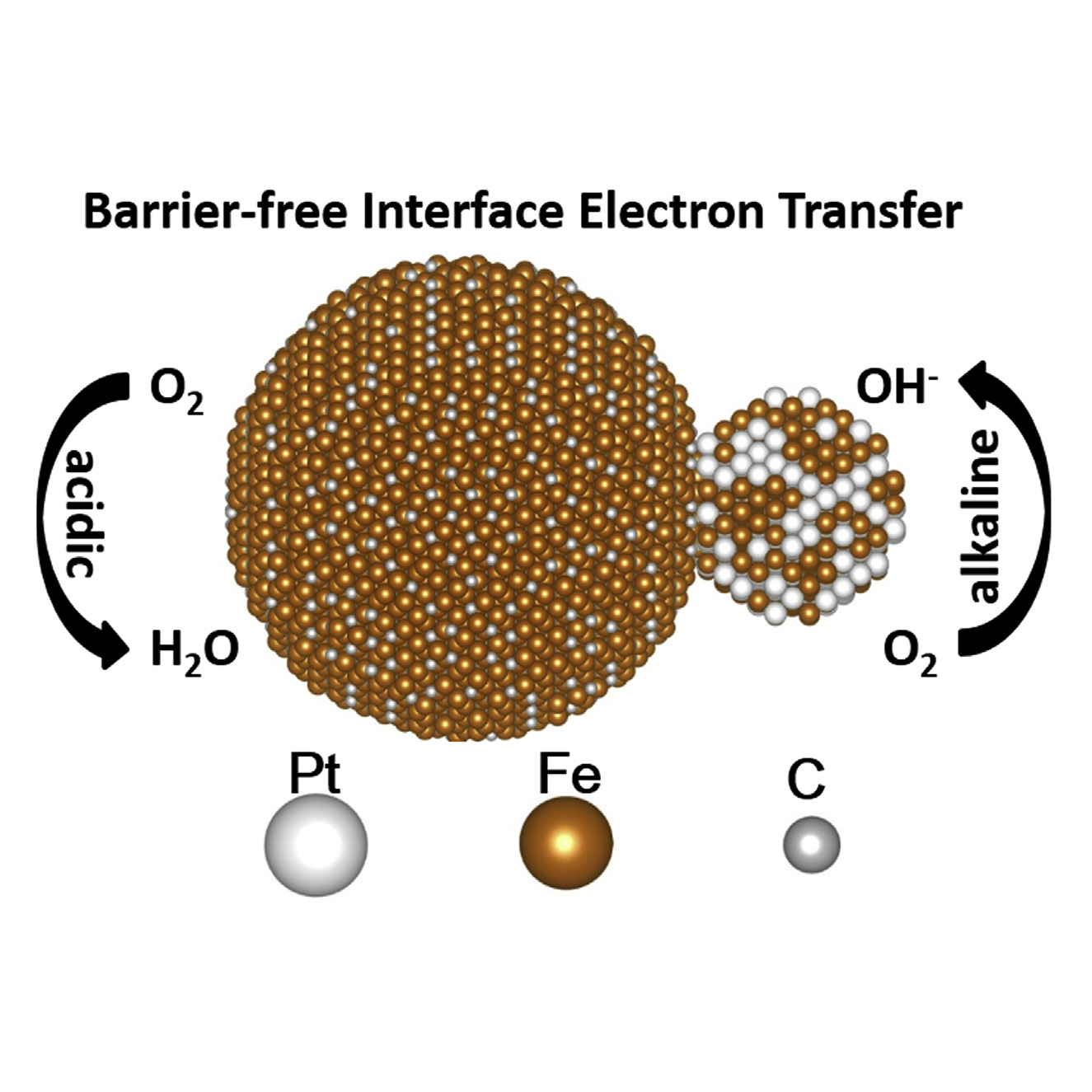
Designing highly efficient interface catalysts with new interface-enhancing mechanisms for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in acid solution still remains a significant challenge. Here, we report a class of stable PtFe-Fe2C Janus- like nanoparticle (NP) interface catalysts with an unrevealed barrier-free interface electron-transfer property that greatly boosts ORR catalytic activity and stability.
The PtFe-Fe2C Janus-like NPs showed much higher catalytic activity for ORR than either PtFe or Fe2C NPs in both acidic and alkaline electrolytes. Density functional theory simulations revealed that a barrier-free interface electron transfer on the interface of PtFe-Fe2C Janus-like NPs is the main factor in enhancing ORR activity. This interface electron-transfer property makes them the most active for ORR among all reported PtFe-based nanocatalysts. We further demonstrate that this barrier-free interface electron-transfer property can be readily generalized to other systems, such as the hydrogen evolution reaction and H2O2 reduction electrocatalysis, to achieve better electrocatalytic enhancement.